The manufacturing industry is constantly evolving. The introduction of new technologies is speeding up and scaling the production of goods. Nowadays, you would not see a factory or a warehouse without machines. For instance, the conveyor belt, which runs with the help of the simple but versatile stepper motor, has been so deeply integrated into manufacturing.
Manufacturing will continue to develop to meet the demands of the market in the coming decades. It is inevitable for new technologies to revolutionize the industry over and over again.
Here is a peek into what the future of the factory will look like.
Robots and Humans Hand in Hand
Automation is the future. Manufacturers around the world are already using robots. Industries have proven that these machines boost efficiency and productivity. While the initial cost is high, the improvements will more than make up for it in the long run. In addition, automation lowers the cost of production.
The Robotic Industries Association reported that, during the third quarter of 2019, there had been an increase of 5.2 percent in robot orders from manufacturers. A total of 23,894 robotic units amounting to $1.3 billion were purchased during that period.
However, unlike what doomsayers have been warning about, robots will not take over, at least for a while. Manufacturing will instead capitalize on so-called “cobots,” collaborative robots that aim to help make the jobs of human workers easier. Cobots allow for incremental progress. While they provide the benefits of robots, they are easier to implement because they are integrated into the process.
It is not just the big corporations that are taking advantage of cobots, either. Increasingly, small and medium manufacturers have also deployed cobots.
Wider Adoption of IoT

The Internet of Things (IoT) will continue to expand in manufacturing. According to a survey, the majority of manufacturers who responded are optimistic about the future of IoT. Nearly all of them (93 percent) believe that its benefits exceed the risks.
IoT in manufacturing involves connecting a spectrum of devices and equipment. They collect massive troves of data and share it with one another, allowing for better monitoring and collaborative action.
Many manufacturers have plans to implement IoT in the next couple of years. The most popular use of IoT devices and equipment in manufacturing are in logistics, supply chain, employee and customer experience, and predictive maintenance.
There is, however, concern over the wide adoption of IoT. Because of the massive data being collected, manufacturers have fears over a breach of their privacy and security. That is why manufacturers need to partner only with trusted organizations to ensure that the devices and equipment they are implementing are impenetrable. Cutting costs, in this case, would only make the organization vulnerable to cybercrimes.
Wearable Devices as Part of the Uniform
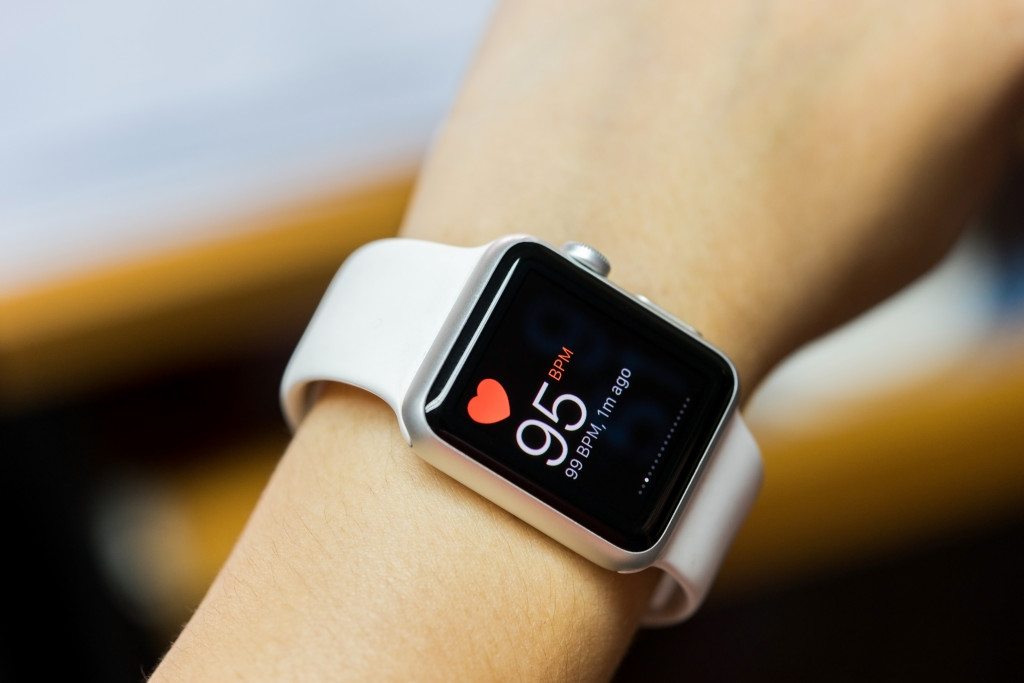

Increasingly, wearables are being adapted in manufacturing, too. The technology can be implemented in various ways to improve processes and ensuring workplace safety. A single smartwatch can monitor a worker’s vitals. It could also send an alert in case a worker has fallen and in need of help. Meanwhile, a pair of smart glasses, which uses augmented reality, can better guide people around hazards, such as spilled fluids on the floor or hot machinery.
Wearables can also be used to improve efficiency. One fulfillment company experimented using smart glasses developed by a leading tech company. Employees wore the high-tech lenses to pick and prepare products. The company reported a 15 percent boost in speed, while error declined by 12 percent.
In addition, wearables can aid in on-site training without using sensitive and dangerous equipment. A pair of smart lenses can correct the problem by creating opportunities for new workers to practice without handling the equipment. These smart glasses have also been implemented to make the training of new workers safer and more effective.
Utilization of 5G
As manufacturing becomes more and more reliant on technology, the necessity of 5G becomes clearer. The integration of IoT, wearables, and robotics will require high-speed internet to collect and pass on the data from different parts of the manufacturing process. The manufacturing facility will have more demands for bandwidth to make way for a stable and reliable connection. Without it, upgrading to new technology would be a waste of time and resources.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is happening now. Manufacturers are finally recognizing the importance and potential of a connected, intelligent, and computerized system to improve efficiency and ensure that the organization reaches the required output.
The trends point toward a wider use of different technologies in manufacturing. Those that have already adopted robots, IoT, and wearables are already reaping the benefits.
